
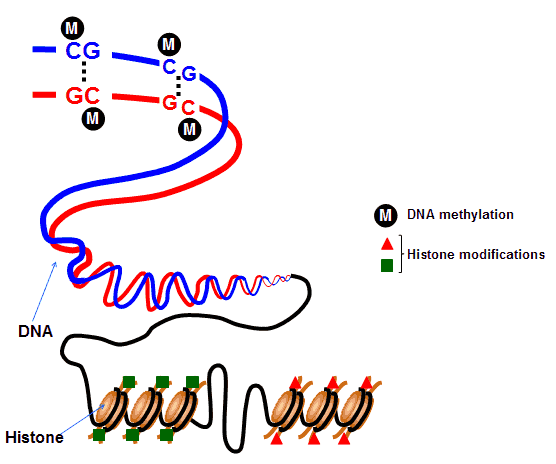
DNA methylation involve the cytosine and adenine, which are two of the four bases of DNA. This modification can also be transferred and inherited through cell division. DNA is normally removed during the occurrence in a zygote formation and are re-developed through successive cell divisions. DNA methylation alters the patten in cells so that cells can "remember where they have been" or have a decrease in gene expression. DNA methylation is also known to supress and increase the expression of viral genes and have incorporated into the genome of the individual over time. Since DNA methylation forms the basis of chromatin structures, it enables a cell to form multiple characteristics neccessary for multicellular life. DNA methylation is known to a play a crucial role in the development of almost all the types of cancer. (14)
"DNA methylation is a process by which a cell can modify its DNA in order to alter expression of a given genes product, usually a protein. DNA methylation is termed a chemical modification which initially thought to only be an inherited property of our DNA. DNA methylation modifications can be altered without affecting the DNA sequence remarkable. There is no change in the genetic code with the addition or removal of DNA methylation modifications. Rather than affecting the genetic code, which is the blueprint, DNA methylation affects the epigenetic code, the expression of the blueprint." (28)
DNA Methylation

Left: (Image 23)